Chapter 12 Kinetics
12.1 Chemical Reaction Rates
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define chemical reaction rate
- Derive rate expressions from the balanced equation for a given chemical reaction
- Calculate reaction rates from experimental data
A rate is a measure of how some property varies with time. Speed is a familiar rate that expresses the distance traveled by an object in a given amount of time. Wage is a rate that represents the amount of money earned by a person working for a given amount of time. Likewise, the rate of a chemical reaction is a measure of how much reactant is consumed, or how much product is produced, by the reaction in a given amount of time.
The rate of reaction is the change in the amount of a reactant or product per unit time. Reaction rates are therefore determined by measuring the time dependence of some property that can be related to reactant or product amounts. Rates of reactions that consume or produce gaseous substances, for example, are conveniently determined by measuring changes in volume or pressure. For reactions involving one or more colored substances, rates may be monitored via measurements of light absorption. For reactions involving aqueous electrolytes, rates may be measured via changes in a solution’s conductivity.
For reactants and products in solution, their relative amounts (concentrations) are conveniently used for purposes of expressing reaction rates. For example, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, in an aqueous solution changes slowly over time as it decomposes according to the following equation:
2 H2O2(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + O2(g)
The rate at which the hydrogen peroxide decomposes can be expressed in terms of the rate of change of its concentration, as shown here:
This mathematical representation of the change in species concentration over time is the rate expression for the reaction. The brackets indicate molar concentrations, and the symbol delta (Δ) indicates “change in.” [H2O2]t1 represents the molar concentration of hydrogen peroxide at some time t1, [H2O2]t2 represents the molar concentration of hydrogen peroxide at a later time t2, and Δ[H2O2] represents the change in molar concentration of hydrogen peroxide during the time interval Δt (that is, t2 − t1). Since the reactant concentration decreases as the reaction proceeds, Δ[H2O2] is a negative quantity. Reaction rates are, by convention, positive quantities, and so this negative change in concentration is multiplied by −1. Figure 12.2 provides an example of data collected during the decomposition of H2O2.
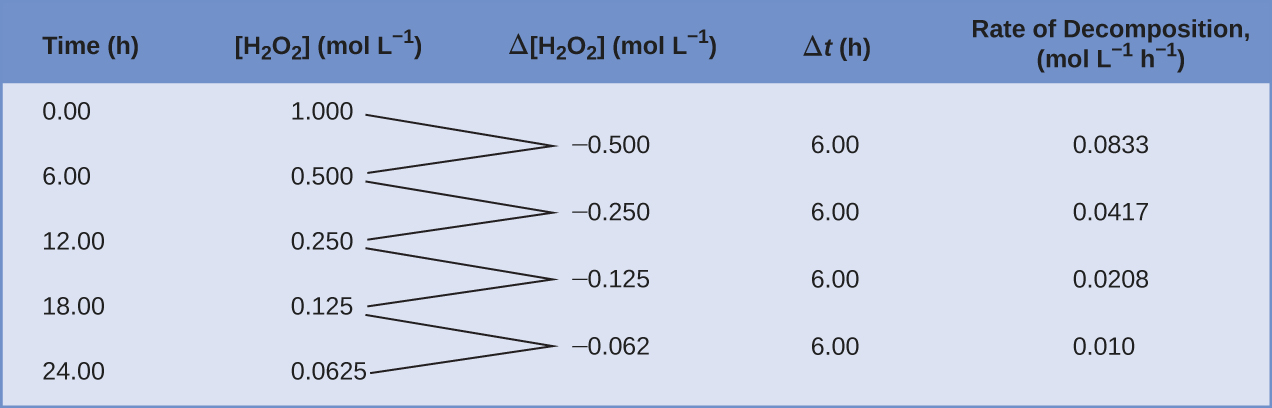
To obtain the tabulated results for this decomposition, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide was measured every 6 hours over the course of a day at a constant temperature of 40°C. Reaction rates were computed for each time interval by dividing the change in concentration by the corresponding time increment, as shown here for the first 6-hour period:
Notice that the reaction rates vary with time, decreasing as the reaction proceeds. Results for the last 6-hour period yield a reaction rate of:
This behavior indicates the reaction continually slows with time. Using the concentrations at the beginning and end of a time period over which the reaction rate is changing (like in Figure 12.2 and the reaction rates calculated above) results in the calculation of an average rate for the reaction over this time interval. At any specific time, the rate at which a reaction is proceeding is known as its instantaneous rate. The instantaneous rate of a reaction at “time zero,” when the reaction commences, is its initial rate.
Consider the analogy of a car slowing down as it approaches a stop sign. The vehicle’s initial rate—analogous to the beginning of a chemical reaction—would be the speedometer reading at the moment the driver begins pressing the brakes (t0). A few moments later, the instantaneous rate at a specific moment—call it t1—would be somewhat slower, as indicated by the speedometer reading at that point in time. As time passes, the instantaneous rate will continue to fall until it reaches zero, when the car (or reaction) stops. Unlike instantaneous speed, the car’s average speed is not indicated by the speedometer; but it can be calculated as the ratio of the distance traveled to the time required to bring the vehicle to a complete stop (Δt). Like the decelerating car, the average rate of a chemical reaction will fall somewhere between its initial and final rates.
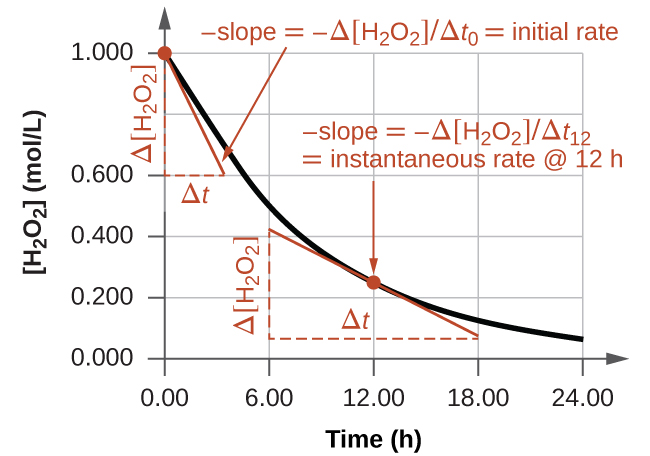
The instantaneous rate of a reaction may be determined one of two ways. If experimental conditions permit the measurement of concentration changes over very short time intervals, then average rates computed as described earlier provide reasonably good approximations of instantaneous rates. Alternatively, a graphical procedure may be used that, in effect, yields the results that would be obtained if short time interval measurements were possible. In a plot of the concentration of hydrogen peroxide against time, the instantaneous rate of decomposition of H2O2 at any time t is given by the slope of a straight line that is tangent to the curve at that time (Figure 12.3). These tangent line slopes may be evaluated using calculus, but the procedure for doing so is beyond the scope of this chapter.
Chemistry in Everyday Life
Reaction Rates in Analysis: Test Strips for Urinalysis
Physicians often use disposable test strips to measure the amounts of various substances in a patient’s urine (Figure 12.4). These test strips contain various chemical reagents, embedded in small pads at various locations along the strip, which undergo changes in color upon exposure to sufficient concentrations of specific substances. The usage instructions for test strips often stress that proper read time is critical for optimal results. This emphasis on read time suggests that kinetic aspects of the chemical reactions occurring on the test strip are important considerations.
The test for urinary glucose relies on a two-step process represented by the chemical equations shown here:
The first equation depicts the oxidation of glucose in the urine to yield glucolactone and hydrogen peroxide. The hydrogen peroxide produced subsequently oxidizes colorless iodide ion to yield brown iodine, which may be visually detected. Some strips include an additional substance that reacts with iodine to produce a more distinct color change.
The two test reactions shown above are inherently very slow, but their rates are increased by special enzymes embedded in the test strip pad. This is an example of catalysis, a topic discussed later in this chapter. A typical glucose test strip for use with urine requires approximately 30 seconds for completion of the color-forming reactions. Reading the result too soon might lead one to conclude that the glucose concentration of the urine sample is lower than it actually is (a false-negative result). Waiting too long to assess the color change can lead to a false positive due to the slower (not catalyzed) oxidation of iodide ion by other substances found in urine.

Relative Rates of Reaction
The rate of a reaction may be expressed as the change in concentration of any reactant or product. For any given reaction, these rate expressions are all related simply to one another according to the reaction stoichiometry. The rate of the general reaction is as follows:
This can be expressed in terms of the decrease in the concentration of A or the increase in the concentration of B. These two rate expressions are related by the stoichiometry of the reaction:
Consider the reaction represented by the following equation:
The relation between the reaction rates expressed in terms of nitrogen production and ammonia consumption, for example, is:
This may be represented in an abbreviated format by omitting the units of the stoichiometric factor:
Note that a negative sign has been included as a factor to account for the opposite signs of the two amount changes (the reactant amount is decreasing while the product amount is increasing). For homogeneous reactions, both the reactants and products are present in the same solution and thus occupy the same volume, so the molar amounts may be replaced with molar concentrations:
Similarly, the rate of formation of H2 is three times the rate of formation of N2 because three moles of H2 are produced for each mole of N2 produced.
Figure 12.5 illustrates the change in concentrations over time for the decomposition of ammonia into nitrogen and hydrogen at 1100°C. Slopes of the tangent lines at t = 500 s show that the instantaneous rates derived from all three species involved in the reaction are related by their stoichiometric factors. The rate of hydrogen production, for example, is observed to be three times greater than that for nitrogen production:
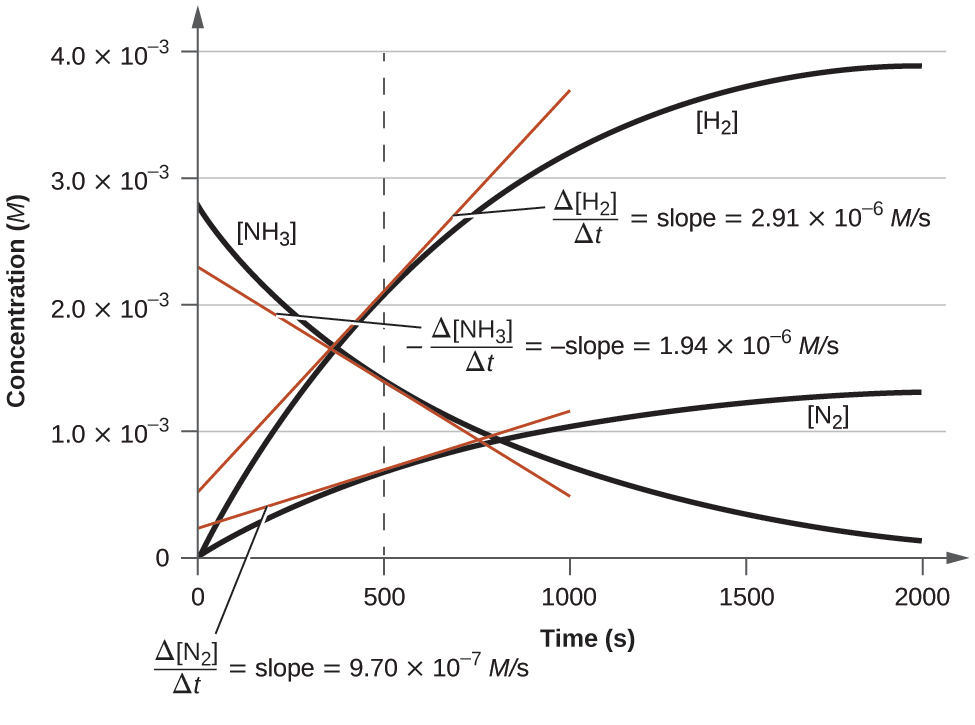
The rates of change of the three concentrations are related by the reaction stoichiometry, as shown by the different slopes of the tangents at t = 500 s.
Example 12.1 – Expressions for Relative Reaction Rates
The first step in the production of nitric acid is the combustion of ammonia:
Write the equations that relate the rates of consumption of the reactants and the rates of formation of the products.
Solution
Considering the stoichiometry of this homogeneous reaction, the rates for the consumption of reactants and formation of products are:
Check Your Learning
The rate of formation of Br2 is 6.0 × 10−6 (mol/L)/s in a reaction described by the following net ionic equation:
Which of the rate expressions below does not represent the rate of this reaction?
Example 12.2 – Reaction Rate Expressions for Decomposition of H2O2
The graph in Figure 12.3 shows the rate of the decomposition of H2O2 over time:
Based on these data, the instantaneous rate of decomposition of H2O2 at t = 11.1 h is determined to be 3.20 × 10−2 (mol/L)/h, that is:
What is the instantaneous rate of production of H2O and O2?
Solution
The reaction stoichiometry shows that:
Therefore:
Check Your Learning
Click here to see this problem worked through!
The equation for the decomposition of ammonia to nitrogen and hydrogen gas is:
2 NH3 → N2 + 3 H2
The reaction stoichiometry shows that:
The rate of production of nitrogen is therefore:
and the rate of production of hydrogen is:
