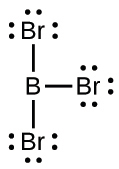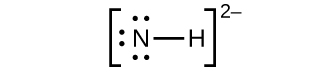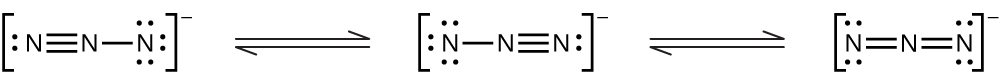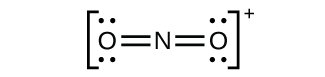Answer Keys to Selected Problems
Chapter 18 Key
18.1. The alkali metals all have a single s electron in their outermost shell. In contrast, the alkaline earth metals have a completed s subshell in their outermost shell. In general, the alkali metals react faster and are more reactive than the corresponding alkaline earth metals in the same period.
18.5. The possible ways of distinguishing between the two include infrared spectroscopy by comparison of known compounds, a flame test that gives the characteristic yellow color for sodium (strontium has a red flame), or comparison of their solubilities in water. At 20°C, NaCl dissolves to the extent of [latex]\frac {35.7 \: g}{100 \: mL}[/latex] compared with [latex]\frac {53.8 \: g}{100 \: mL}[/latex] for SrCl2. Heating to 100°C provides an easy test, since the solubility of NaCl is [latex]\frac {39.12 \: g}{100 \: mL}[/latex], but that of SrCl2 is [latex]\frac {100.8 \: g}{100 \: mL}[/latex]. Density determination on a solid is sometimes difficult, but there is enough difference (2.165 g/mL NaCl and 3.052 g/mL SrCl2) that this method would be viable and perhaps the easiest and least expensive test to perform.
(a) 2 Sr(s) + O2(g) → 2 SrO(s)
(b) Sr(s) + 2 HBr(g) → SrBr2(s) + H2(g)
(c) Sr(s) + H2(g) → SrH2(s)
(d) 6 Sr(s) + P4(s) → 2 Sr3P2(s)
(e) Sr(s) + 2 H2O(l) → Sr(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
18.11. Yes, tin reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen gas.
18.13. In PbCl2, the bonding is ionic, as indicated by its melting point of 501°C. In PbCl4, the bonding is covalent, as evidenced by it being an unstable liquid at room temperature.
18.15. 2 CsCl(l) + Ca(g) [latex]\xrightarrow {countercurrent \; fractionating \; tower}[/latex] 2 Cs(g) + CaCl2(l)
Cathode (reduction): 2 Li+ + 2 e− → 2 Li(l)
Anode (oxidation): 2 Cl− → Cl2(g) + 2 e−
Overall reaction: 2 Li+ + 2 Cl− → 2 Li(l) + Cl2(g)
18.21. Despite its reactivity, magnesium can be used in construction even when the magnesium is going to come in contact with a flame because a protective oxide coating is formed, preventing gross oxidation. Only if the metal is finely subdivided or present in a thin sheet will a high-intensity flame cause its rapid burning.
Extract from ore: AlO(OH)(s) + NaOH(aq) + H2O(l) → NaAl(OH)4(aq)
Recover: 2 NaAl(OH)4(s) + H2SO4(aq) → 2 Al(OH)3(s) + Na2SO4(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
Sinter: 2 Al(OH)3(s) → Al2O3(s) + 3 H2O(g)
Dissolve in Na3AlF6(l) and electrolyze: Al3+ + 3 e− → Al(s)
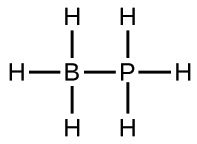
(a) H3BPH3:
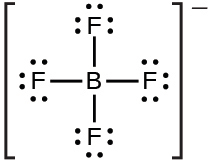
(b) BF4−:
(c) BBr3:
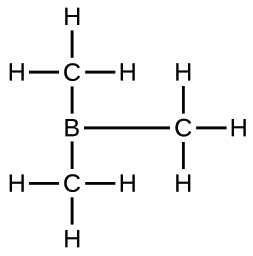
(d) B(CH3)3:
(e) B(OH)3:
18.33. (a) (CH3)3SiH: sp3 bonding about Si; the structure is tetrahedral (b) SiO44−: sp3 bonding about Si; the structure is tetrahedral (c) Si2H6: sp3 bonding about each Si; the structure is linear along the Si-Si bond (d) Si(OH)4: sp3 bonding about Si; the structure is tetrahedral (e) SiF62−: sp3d 2 bonding about Si; the structure is octahedral
18.35. (a) nonpolar (b) nonpolar (c) polar (d) nonpolar (e) polar
18.37. (a) tellurium dioxide or tellurium (IV) oxide (b) antimony (III) sulfide (c) germanium (IV) fluoride (d) silane or silicon (IV) hydride (e) germanium (IV) hydride
18.39. Boron has only s and p orbitals available, which can accommodate a maximum of four electron pairs. Unlike silicon, no d orbitals are available in boron.
18.41. (a) ΔH° = 87 kJ, ΔG° = 44 kJ (b) ΔH° = −109.9 kJ, ΔG° = −154.7 kJ (c) ΔH° = −510 kJ, ΔG° = −601.5 kJ
18.43. A mild solution of hydrofluoric acid would dissolve the silicate and would not harm the diamond.
18.45. In the N2 molecule, the nitrogen atoms have an σ bond and two π bonds holding the two atoms together. The presence of three strong bonds makes N2 a very stable molecule. Phosphorus is a third-period element, and as such, does not form π bonds efficiently; therefore, it must fulfill its bonding requirement by forming three σ bonds.
18.47. (a) H = 1+, C = 2+, and N = 3− (b) O = 2+ and F = 1− (c) As = 3+ and Cl = 1−
18.51. The electronegativity of the nonmetals is greater than that of hydrogen. Thus, the negative charge is better represented on the nonmetal, which has the greater tendency to attract electrons in the bond to itself.
18.53. Hydrogen has only one orbital with which to bond to other atoms. Consequently, only one two-electron bond can form.
(a) Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
(b) CaO(s) + SO2(g) → CaSO3(s)
(c) 2 NaHCO3(s) + NaH2PO4(aq) → Na3PO4(aq) + 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l)
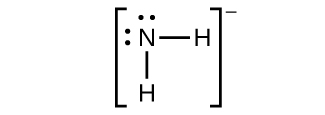
(a) NH2−:
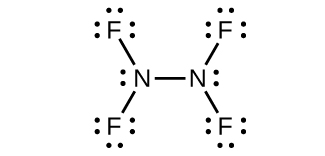
(b) N2F4:
(c) NH2−:
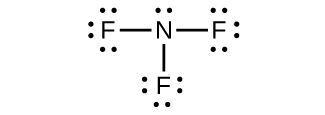
(d) NF3:
(e) N3−:
18.61. Ammonia acts as a Brønsted base because it readily accepts protons and as a Lewis base because it has an electron pair to donate.
Brønsted base: NH3 + H3O+ → NH4+ + H2O
Lewis base: 2 NH3 + Ag+ → [H3N−Ag−NH3]+
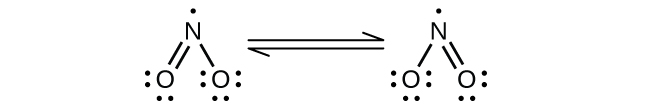
(a) NO2:
Nitrogen is sp2 hybridized. The molecule has a bent geometry with an ONO bond angle of approximately 120°.
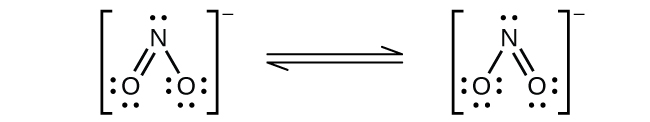
(b) NO2−:
Nitrogen is sp2 hybridized. The molecule has a bent geometry with an ONO bond angle slightly less than 120°.
(c) NO2+:
Nitrogen is sp hybridized. The molecule has a linear geometry with an ONO bond angle of 180°.
18.65. Nitrogen cannot form a NF5 molecule because it does not have d orbitals to bond with the additional two fluorine atoms.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(a) P4(s) + 4 Al(s) → 4 AlP(s)
(b) P4(s) + 12 Na(s) → 4 Na3P(s)
(c) P4(s) + 10 F2(g) → 4 PF5(l)
(d) P4(s) + 6 Cl2(g) → 4 PCl3(l) or P4(s) + 10 Cl2(g) → 4 PCl5(l)
(e) P4(s) + 3 O2(g) → P4O6(s) or P4(s) + 5 O2(g) → P4O10(s)
(f) P4O6(s) + 2 O2(g) → P4O10(s)
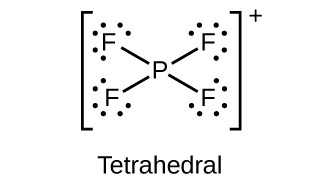
(a)
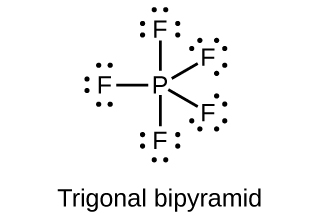
(b)
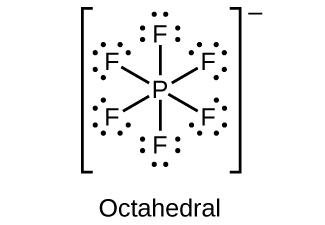
(c)
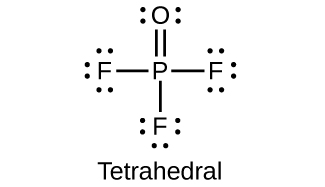
(d)
18.77. (a) P = 3+ (b) P = 5+ (c) P = 3+ (d) P = 5+ (e) P = 3− (f) P = 5+
(a) 2 Zn(s) + O2(g) → 2 ZnO(s)
(b) ZnCO3(s) → ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
(c) ZnCO3(s) + 2 CH3COOH(aq) → Zn(CH3COO)2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
(d) Zn(s) + 2 HBr(aq) → ZnBr2(aq) + H2(g)
18.83. Al(OH)3(s) + 3 H+(aq) → Al3+ + 3 H2O(l) Al(OH)3(s) + OH− → Al(OH)4−(aq)
(a) Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2 NaOH(aq)
(b) Cs2CO3(s) + 2 HF(aq) → 2 CsF(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
(c) Al2O3(s) + 6 HClO4(aq) → 2 Al(ClO4)3(aq) + 3 H2O(l)
(d) Na2CO3(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) → 2 NaNO3(aq) + BaCO3(s)
(e) TiCl4(l) + 4 Na(s) → Ti(s) + 4 NaCl(s)
18.87. HClO4 is the stronger acid because, in a series of oxyacids with similar formulas, the higher the electronegativity of the central atom, the stronger is the attraction of the central atom for the electrons of the oxygen(s). The stronger attraction of the oxygen electron results in a stronger attraction of oxygen for the electrons in the O-H bond, making the hydrogen more easily released. The weaker this bond, the stronger the acid.
18.89. As H2SO4 and H2SeO4 are both oxyacids and their central atoms both have the same oxidation number, the acid strength depends on the relative electronegativity of the central atom. As sulfur is more electronegative than selenium, H2SO4 is the stronger acid.
18.91. SO2, sp2 4+ SO3, sp2, 6+ H2SO4, sp3, 6+
18.93. SF6: S = 6+ SO2F2: S = 6+ KHS: S = 2−
18.95. Sulfur is able to form double bonds only at high temperatures (substantially endothermic conditions), which is not the case for oxygen.
18.97. There are many possible answers, including Cu(s) + 2 H2SO4(l) → CuSO4(aq) + SO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) and C(s) + 2 H2SO4(l) → CO2(g) + 2 SO2(g) + 2 H2O(l)
18.101 SnCl4 is not a salt because it is covalently bonded. A salt must have ionic bonds.
18.103. In oxyacids with similar formulas, the acid strength increases as the electronegativity of the central atom increases. HClO3 is stronger than HBrO3; Cl is more electronegative than Br.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
18.107. (a) bromine trifluoride (b) sodium bromate (c) phosphorus pentabromide (d) sodium perchlorate (e) potassium hypochlorite
18.109. (a) I: 7+ (b) I: 7+ (c) Cl: 4+ (d) I: 3+, Cl: 1− (e) F: 0
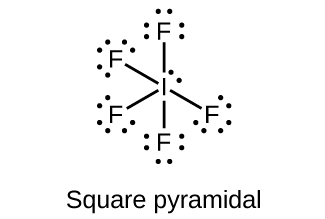
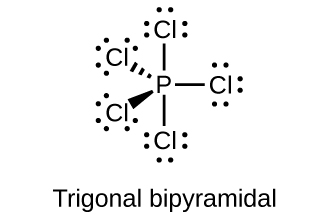
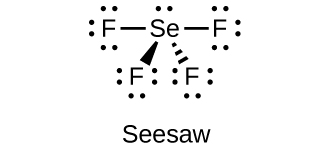
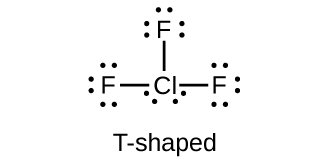
18.111. (a) sp3d hybridized (b) sp3d 2 hybridized (c) sp3 hybridized (d) sp3 hybridized (e) sp3d 2 hybridized
18.113. (a) nonpolar (b) nonpolar (c) polar (d) nonpolar (e) polar
18.115. The empirical formula is XeF6, and the balanced reactions are:
Xe(g) + 3 F2(g) [latex]\rightarrow {\Delta}[/latex] XeF6(s)
XeF6(s) + 3 H2(g) → 6 HF(g) + Xe(g)