22 Acknowledging and Citing Generative AI in Academic Work
Overview
In this chapter, you’ll think through when and how to cite the use of generative AI tools in your academic work. You will see how the MLA and APA require writers to cite generative AI and review some example citations.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this chapter, you’ll be able to:
- Decide whether to use generative AI tools in specific contexts
- Identify different models for citing generative AI tools
- Create an appropriate citation for the use of generative AI tools
You’ve already learned the importance of citing your sources in academic work, but how do you cite generative AI tools like ChatGPT?
Before we get started, it’s important to remember that not all instructors allow students to use generative AI in their assignments. You should check with your instructor before using AI in any class. When in doubt, ask!
Before You Use Generative AI, Consider How and Why You’re Using It
As an instructor and a writer, I have found that generative artificial intelligence tools can be helpful for exploring ideas, refining research questions, outlining arguments, and breaking down difficult concepts for students. When my students use ChatGPT, I ask them to include a citation (How to Cite ChatGPT [Website]) for the tool they used. I also ask them to provide a brief description of how they used ChatGPT and how they checked the accuracy of its output. Let’s review an example of this from Luka Denney’s essay [Website] in Beginnings and Endings, a student-created open education resource:
For this essay, I used Chat GPT as a resource to give me a summary of the feminist and queer theory analysis lens. “Feminist queer theory is a critical analysis lens that combines feminist theory and queer theory to examine how gender and sexuality intersect and shape social power dynamics. This approach challenges the dominant cultural norms that promote heteronormativity, gender binary, and patriarchy, which result in marginalizing individuals who do not conform to these norms.” With this, it helped me better understand the material so I could write better essays. This information was accessed on May 6th, 2023. (Denney)
Reflecting on how and why you are using generative AI can help you to ensure that you are not plagiarizing.
Luka’s reflection is an example of an acknowledgement statement, which is separate from a citation. Increasingly, students should become familiar with AI acknowledgement statements and clarify with their instructors when these statements are needed.
Suggestions for Acknowledging Use of AI
Monash University provides helpful recommendations (Acknowledging the use of Artificial Intelligence [Website]) for how to acknowledge when and how you’ve used generated material as part of an assignment or project. If you decide to use generative artificial intelligence such as ChatGPT for an assignment, you should include a statement that does the following:
- Provides a written acknowledgment of the use of generative artificial intelligence
- Specifies which technology was used
- Includes explicit descriptions of how the information was generated
- Identifies the prompts used
- Explains how the output was used in your work
The template Monash University provides is also helpful. Students may include this information either in a cover letter or in an appendix to the submitted work.
I acknowledge the use of [insert AI system(s) and link] to [specific use of generative artificial intelligence]. The prompts used include [list of prompts]. The output from these prompts was used to [explain use].
Academic style guides such as APA already include guidelines for including appendices after essays and reports. Review Purdue Owl’s entry on Footnotes and Appendices [Website] for help.
Citing AI Chatbots
In some situations, students may want to cite information from a chatbot conversation, such as a definition or discussion of a concept they want to use in an essay. The American Psychological Association (APA) and the Modern Language Association (MLA), two of the most frequently used style guides for college writing, have both provided guidelines for how to do this.
ChatGPT has the ability to share links (ChatGPT Shared Links FAQ [Website]) to specific chats. It’s best practice to include those links in your reference. For other tools like Google Docs’ Writing Assistant, links are not yet available, so it’s important to be transparent with your reader about how and when you are using AI in your writing.
Here’s an example of a shared chat link in ChatGPT 3.5 [Website]. When you click on the link, you’ll be able to see both the author’s prompts and the chatbot’s responses. Including links provides transparency for your writing process.
APA Style
Review the example below to see how the American Psychological Association [Website] (APA) formats ChatGPT citations:
When prompted with “Is the left brain right brain divide real or a metaphor?” the ChatGPT-generated text indicated that, although the two brain hemispheres are somewhat specialized, “the notation that people can be characterized as ‘left-brained’ or ‘right-brained’ is considered to be an oversimplification and a popular myth” (OpenAI, 2023).
Citation:
OpenAI. (2023). ChatGPT [Website] (Mar 14 version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
MLA Style
The Modern Language Association (MLA) uses a template of core elements to create citations for a Works Cited page. MLA [Website] asks students to apply this approach when citing any type of generative AI in their work. They provide the following guidelines:
- Cite a generative AI tool whenever you paraphrase, quote, or incorporate into your own work any content (whether text, image, data, or other) that was created by it.
- Acknowledge all functional uses of the tool (like editing your prose or translating words) in a note, your text, or another suitable location.
- Take care to vet the secondary sources it cites (MLA).
Here are some examples of how to use and cite generative AI with MLA style:
Example One: Paraphrasing Text
Let’s say that I am trying to generate ideas for a paper on Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s short story “The Yellow Wallpaper.” I ask ChatGPT to provide me with a summary and identify the story’s main themes. Here’s a link to the chat [Website]. I decide that I will explore the problem of identity and self-expression in my paper.
My Paraphrase of ChatGPT with In-Text Citation
The suppression of identity and self-expression, especially for nineteenth-century women, is a major theme in “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman (“Summarize the short story”).
Works Cited Entry
“Summarize the short story “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman. Include a breakdown of the main themes” [Website] prompt. ChatGPT. 24 May Version, OpenAI, 20 Jul. 2023, https://chat.openai.com/share/d1526b95-920c-48fc-a9be-83cd7dfa4be5
Example Two: Quoting Text
In the same chat, I continue to ask ChatGPT about the themes of identity and self-expression. Here’s an example of how I could quote the response in the body of my paper:
When I asked ChatGPT to describe the themes of identity and self-expression, it noted that the eponymous yellow wallpaper acts as a symbol of the narrator’s self-repression. However, when prompted to share the scholarly sources that formed the basis of this observation, ChatGPT responded, “As an AI language model, I don’t have access to my training data, but I was trained on a mixture of licensed data, data created by human trainers, and publicly available data. OpenAI, the organization behind my development, has not publicly disclosed the specifics of the individual datasets used, including whether scholarly sources were specifically used” (“Summarize the short story”).
It’s worth noting here that ChatGPT can “hallucinate”[Website] fake sources. As a Microsoft training manual notes, these chatbots are “built to be persuasive, not truthful” (Weiss &Metz, 2023). The May 24, 2023 version will no longer respond to direct requests for references; however, I was able to get around this restriction fairly easily by asking for “resources” instead.
When I ask for resources to learn more about “The Yellow Wallpaper,” here is one source it recommends:
“Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s The Yellow Wallpaper: A Symptomatic Reading” by Elaine R. Hedges: This scholarly article delves into the psychological and feminist themes of the story, analyzing the narrator’s experience and the implications of the yellow wallpaper on her mental state. It’s available in the journal “Studies in Short Fiction.” (“Summarize the short story”).
Using Google Scholar, I look up this source to see if it’s real. Unsurprisingly, this source is not a real one, but my search does lead me to another (real) source: Kasmer, Lisa. “Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s ‘The Yellow Wallpaper’: A Symptomatic Reading.” Literature and Psychology 36.3 (1990): 1.
Note: Always check any sources that ChatGPT or other generative AI tools cite.
A Checklist for Acknowledging and Citing Generative AI Tools
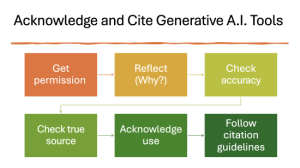
In conclusion, it’s important to follow these five steps if you are considering whether or not to use generative artificial intelligence in your academic work:
-
Check with your instructor to make sure you have permission to use these tools and find out what the limits of that use are.
-
Reflect on how and why you want to use generative AI in your work. If the answer is “to save time” or “so I don’t have to do the work myself,” think about why you are in college in the first place. What skills are you supposed to practice through this assignment? Will a particular use of generative artificial intelligence help you build those skills, or will it get in the way of practice that you need?
-
Check the accuracy of any information provided by a generative artificial intelligence tool against a trusted source. Be especially careful of any sources that generative artificial intelligence provides. Can you verify it? Is anything made up? Would it suit your purpose to cite a more trusted source instead of the AI system?
-
Check whether the AI output is based on a source that should be cited. Chatbots sometimes give answers that reflect a particular source’s text or ideas without citing that source. It’s important to do a search on the topic to see whether the output is accurate and whether further citation is needed.
-
If you decide to use generative artificial intelligence, acknowledge your use in an endnote, an appendix, or a cover letter.
-
Cite any ideas or word sequences that come from generative artificial intelligence, both by mentioning the source in the body of the essay and by citing it on a References or Works Cited page according to the style format your teacher specifies, such as MLA or APA.
These tools are rapidly evolving and have the potential to transform the way we think and write. But much like you can’t solve a math equation with a calculator unless you understand that equation’s steps, you can’t count on quality, accurate output if you “outsource” your thinking and writing to ChatGPT.
Works Cited
Denney, L. “Your Body, Your Choice: At Least, That’s How It Should Be.” Beginnings and Endings: A Critical Edition, 2023, cwi.pressbooks.pub/beginnings-and-endings-a-critical-edition/chapter/feminist-5/.
McAdoo, Timothy. “How to Cite ChatGPT.” APA Style Blog, 7 Apr. 2023, apastyle.apa.org/blog/how-to-cite-chatgpt.
Modern Language Association. “How Do I Cite Generative AI in MLA Style?” MLA Style, 17 Mar. 2023, style.mla.org/citing-generative-ai/.
Monash University. “Acknowledging the Use of Generative Artificial Intelligence.” Monash University Learn HQ, www.monash.edu/learnhq/build-digital-capabilities/create-online/acknowledging-the-use-of-generative-artificial-intelligence.
OpenAI. “Yellow Wallpaper themes.” ChatGPT, 24 May version, 2023. Large Language Model, chat.openai.com/share/70e86a32-6f04-47b4-8ea7-a5aac93c2c77.
Purdue Writing Lab. “Footnotes & Appendices.” Purdue Writing Lab, owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/footnotes_appendices.html.
Weiss, Katherine, and Cade Metz. “When A.I. Chatbots Hallucinate.” The New York Times, 9 May 2023, www.nytimes.com/2023/05/01/business/ai-chatbots-hallucination.html.
Attributions
This chapter was written and remixed by Phil Choong.
This chapter was adapted from “Acknowledging and Citing Generative AI in Academic Work” by Liza Long and is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
“A Checklist for Acknowledging and Citing Generative A.I. Tools” was adapted from “Acknowledging and Citing Generative AI in Academic Work” by Anna Mills and is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Media Attributions
- Yellow Wallpaper Chat
- Acknowledge and Cite Generative AI Tools © Liza Long adapted by Anna Mills is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license

